A urinalysis is a laboratory test for urine. It manages and detects disorders, including urinary tract infections, kidney disease, and diabetes. Additionally, it also involves inspecting the appearance, absorption, and content of urine.
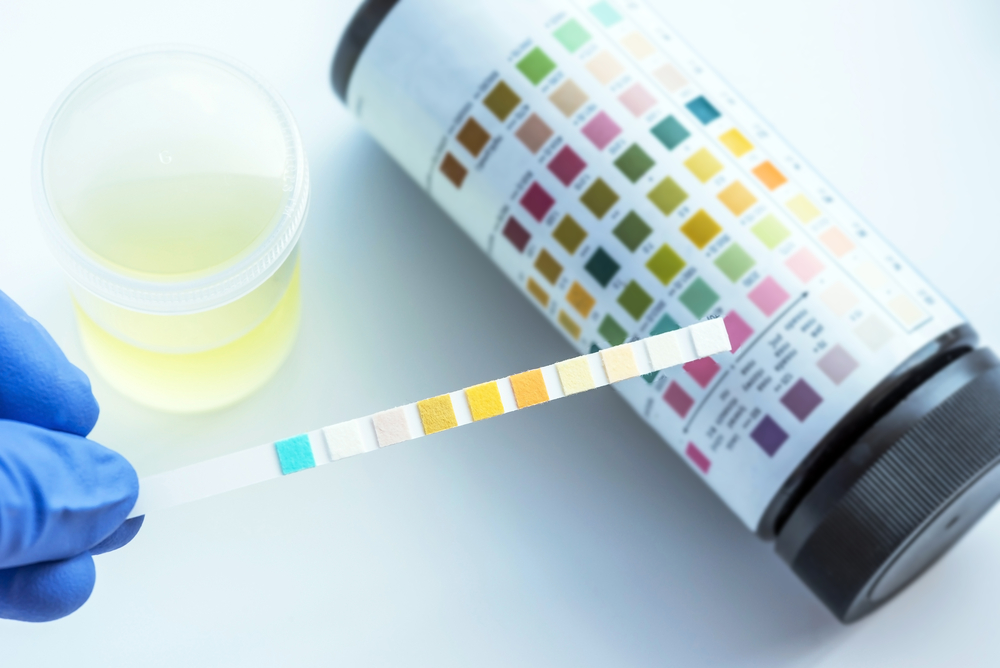
A urinalysis is a laboratory test for urine. It manages and detects disorders, including urinary tract infections, kidney disease, and diabetes. Additionally, it also involves inspecting the appearance, absorption, and content of urine.
SYMPTOMS
A urinalysis is done for the following reasons:
To examine the overall health for:
To diagnose medical conditions such as:
To monitor medical conditions such as:
DIAGNOSIS
You are allowed to eat or drink before the test. Additionally, you must specify the nonprescription medications, vitamins, and other supplements you are taking as these drugs might affect the result.
What To Expect
The doctor will provide a small cup for the urine sample.
It involves the following steps:
To get precise results, use a clean-catch method to avoid catching the bacteria from the sample. However, in some cases, the doctor will insert a thin and flexible tube called a catheter to collect the urine sample.
Afterward, the urine sample is sent to a lab for examination.
Methods Of Urinalysis
The urine sample is evaluated in three ways:
Visual exam: It involves examining the urine’s appearance.
Dipstick test: It is used to detect abnormalities in the urine. It examines the following:
Microscopic exam: This examines the following:
Results
If your results appear normal, the doctor will not require further follow-ups. On the other hand, if your urinalysis results are abnormal, the doctor will require additional tests to locate the cause. Tests may include:
If you encounter severe urine problems, it is best for you to seek medical help.
Overview and FactsTypes and SymptomsDiagnosis & MedicationsOverview and Facts Referred pain is a phenomenon where pain is perceived at a [...]
Overview and FactsTypes and SymptomsDiagnosis & MedicationsOverview and Facts Quinoline yellow is a synthetic food colorant commonly used in the [...]
Overview and FactsTypes and SymptomsDiagnosis & MedicationsOverview and Facts Pneumothorax is a condition characterized by the presence of air in [...]