TYPES
This type of cancer develops in the lining of the blood vessels and lymph vessels.
It can mostly occur in all areas of the body. However, it is a rare form of skin cancer.
Basal cell carcinoma occurs when the skin is too much exposed to sunlight. The most affected body parts are the neck and the head. You can identify basal cell carcinoma when a bump on the skin is slightly transparent.
Cutaneous B-cell lymphoma occurs if white blood cells attack the skin.
Cutaneous B-cell lymphoma has various types. These include:
Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma is another type of lymphoma, and is commonly known as non-hodgkin lymphoma. It is a rare type of skin cancer.
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP) primarily begins in connective tissue cells at the middle layer of your skin (dermis). This is a very rare case of skin cancer.
Merkel cell carcinoma may be identified as a flesh-colored or bluish-red nodule in the face, head or neck.
Sebaceous carcinoma usually starts at the oil glands of the skin. The eyelids are often affected.
Although squamous cell carcinoma is a less life threatening type of skin cancer, immediate treatment is still needed to avoid more serious problems.
Squamous cell carcinoma starts at the middle and outer layers of the skin and can grow in all areas of the body.
SYMPTOMS
Angiosarcoma signs and symptoms include:
Basal cell carcinoma signs and symptoms include:
Cutaneous B-cell lymphoma signs and symptoms include:
Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma signs and symptoms include:
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans signs and symptoms include:
Merkel cell carcinoma signs and symptoms include:
Sebaceous carcinoma signs and symptoms includes:
Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin signs and symptoms includes:
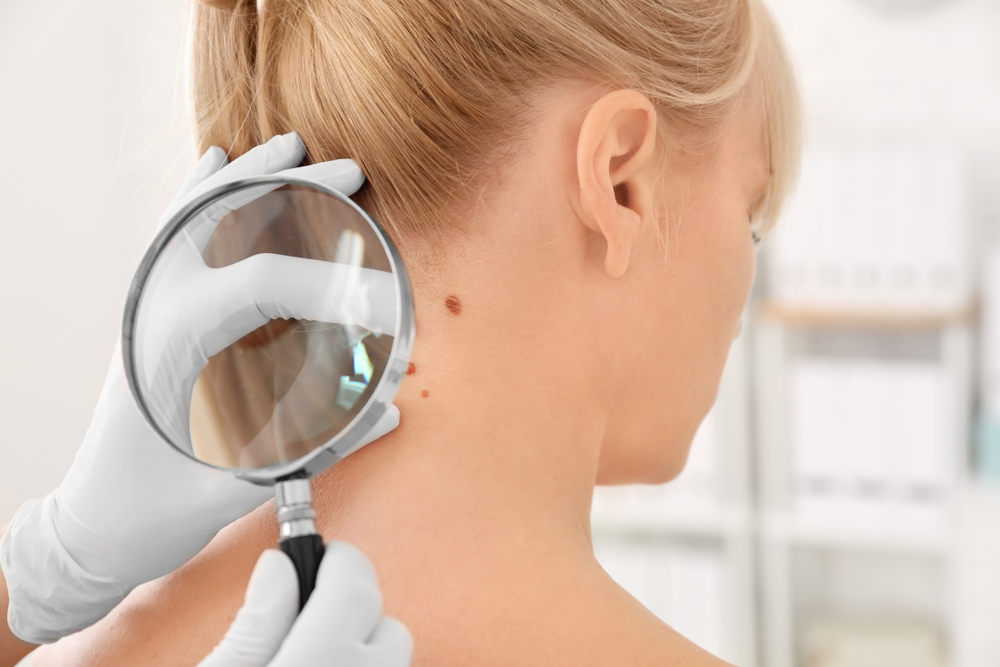
DIAGNOSIS
There are many tests to help your dermatologist diagnose non-melanoma skin cancer. These tests may depend on what type of skin cancer you may have and may include:
TREATMENT
Treatment options may depend on your age, type of skin cancer and underlying medical conditions.
Treatment includes:
Overview and FactsTypes and SymptomsDiagnosis & MedicationsOverview and Facts Tricuspid atresia is a congenital heart defect characterized by the absence [...]
Overview and FactsTypes and SymptomsDiagnosis & MedicationsOverview and Facts Toxic megacolon is a rare but serious complication of inflammatory bowel [...]
Overview and FactsTypes and SymptomsDiagnosis & MedicationsOverview and Facts Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis is a rare but severe and potentially life-threatening [...]