When your body produces excessive thyroid hormone it is called as hyperthyroidism or overactive thyroid.
The frequency, severity and symptoms can differ from one individual to another.
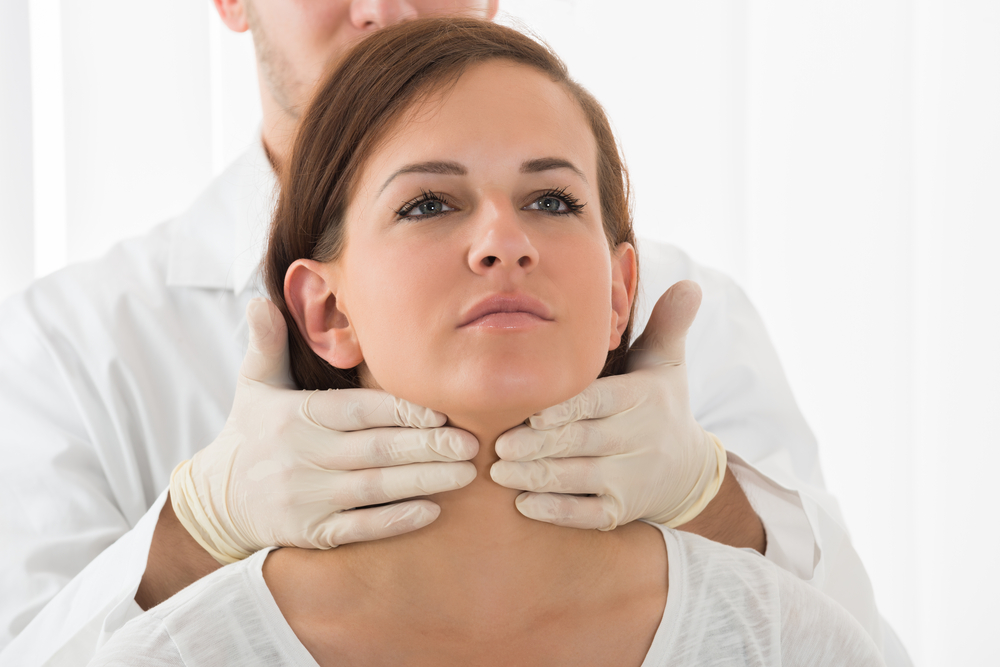
When your body produces excessive thyroid hormone it is called as hyperthyroidism or overactive thyroid.
The frequency, severity and symptoms can differ from one individual to another.
An overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism) has many signs and symptoms, although it is unlikely that you would develop all of them.
Though there are many signs and symptoms of hypothyroidism, a person can’t have all of them
The symptoms of hyperthyroidism are listed below:
Signs of hyperthyroidism
DIAGNOSIS
Hyperthyroidism can be diagnosed by thyroid function tests. These blood tests evaluate the efficiency of your thyroid gland.
In the tests, the levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and thyroid hormones namely, thyroxine and triiodothyronine, will be assessed.
If you have low levels of TSH, you have hyperthyroidism. Too much secretion of thyroid hormones is the reason behind the low levels of TSH.
If you have hyperthyroidism, the levels of thyroxine and triiodothyronine will be high.
Subclinical overactive thyroid gland
In some conditions, your thyroid hormones will be in normal range; however TSH levels will be low. This condition is termed as a subclinical overactive thyroid gland.
This subclinical overactive thyroid gland does not require any treatment as it will get back to normal after few months.
MEDICATIONS/TREATMENT
Hyperthyroidism can be treated with medications. The usual treatment options are listed below:
Thionamides –Methimazole and carbimazole that block the thyroid gland secreting excess thyroid hormone.
Radioiodine treatment – In this method, radioactive iodine is used to reduce thyroid gland activity by shrinking it.
Surgery– In very few cases, surgery can be performed to eliminate a part or whole of the thyroid gland, especially if the person has a large goiter.
Overview and FactsTypes and SymptomsDiagnosis & MedicationsOverview and Facts Referred pain is a phenomenon where pain is perceived at a [...]
Overview and FactsTypes and SymptomsDiagnosis & MedicationsOverview and Facts Quinoline yellow is a synthetic food colorant commonly used in the [...]
Overview and FactsTypes and SymptomsDiagnosis & MedicationsOverview and Facts Pneumothorax is a condition characterized by the presence of air in [...]