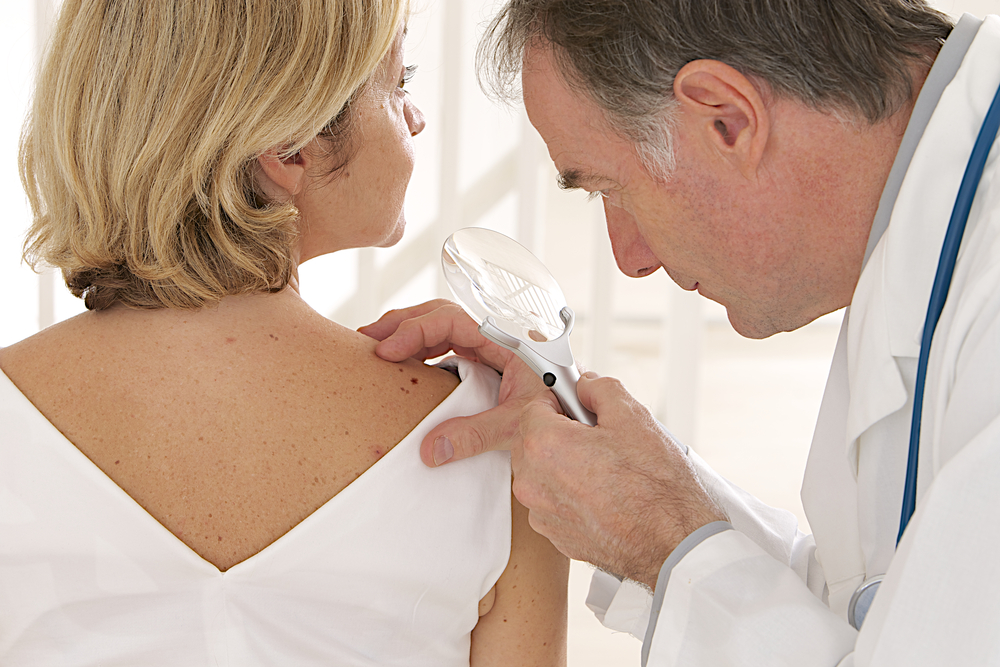
Malignant melanoma is the most severe type of skin cancer that evolves from the pigment-producing cells called melanocytes. It occurs anywhere on the body, typically in areas with more exposure to the sun, such as the face, arms, legs, and back. It may more likely occur in people with fairer skin and those who live closer to the equator. Additionally, this condition may also appear in regions that do not have much sun exposure, such as the palm of your hands, fingernail beds, and feet.
The leading cause of melanoma is DNA damage resulting from ultraviolet light exposure and genetics. People with several moles, a history of affected family members, and a weak immune system have greater risks of developing this type of cancer.