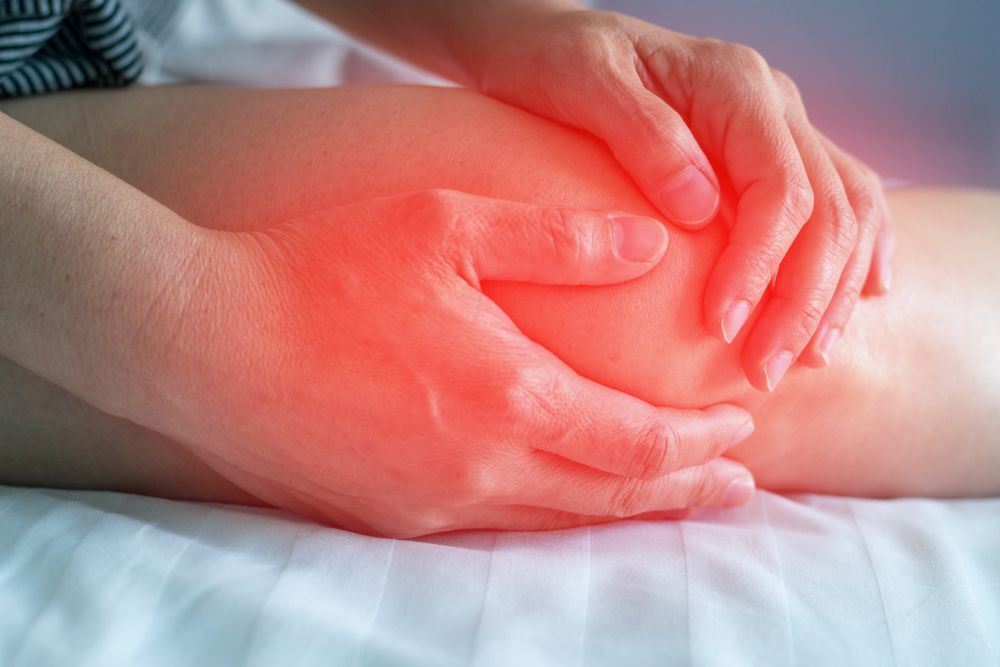
Iliotibial Band Syndrome (ITBS) is a common knee injury caused by inflammation on the lateral knee due to overuse, and frequent friction on the iliotibial band. The pain is at most extensive when the knee is at 30-degree flexion.
Iliotibial band syndrome results from a combination of issues including poor training habits, poor muscle flexibility, prior injury, and other mechanical imbalances in the body. ITBS is most associated with activities that require too much friction and bending of the knee, such as cycling, long-distance running, and weightlifting.
People who are at risk for ITBS are athletes, runners, cyclists, and hikers. Athletes whose activities require a lot of knee movements are likely to develop ITBS. People who also exercise regularly are also at risk, especially when they commit training mistakes such as: not properly warming up or cooling down, straining the body, wearing improper shoes, training on wrong surfaces, using poor form, etc.