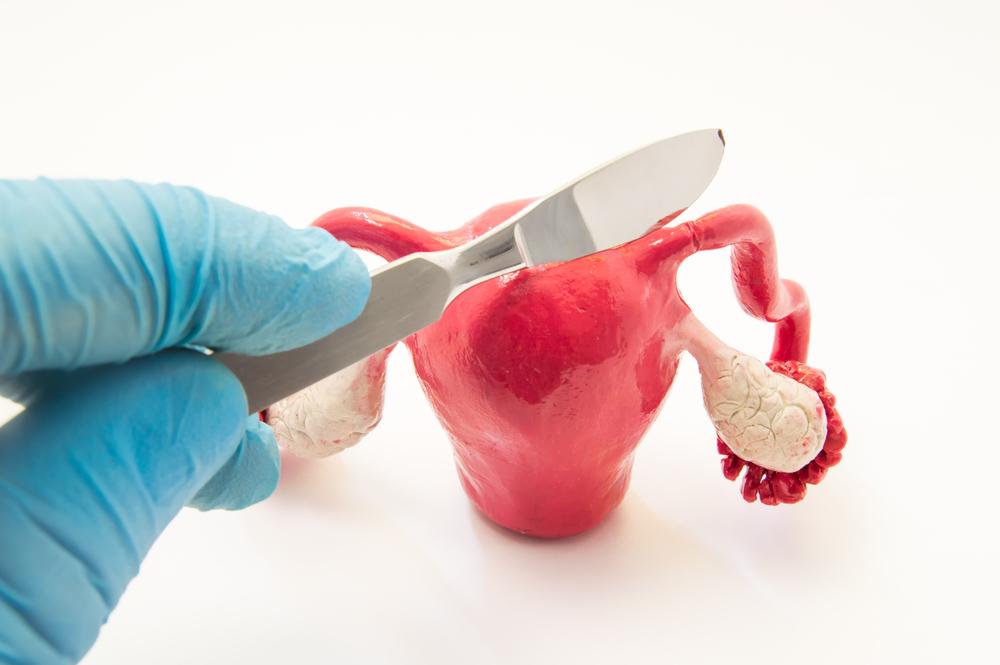
Fallopian tube removal or salpingectomy is a surgical procedure for removal of the diseased fallopian tubes in females. It can be done alone or combined with other procedures like oophorectomy (ovary removal), hysterectomy (uterus removal), and cesarean section (C-section).
When two people have intercourse, and the sperm cell successfully meets the egg cell in the fallopian tube, fertilization occurs. Once this takes place, the zygote (or a newly fertilized cell) moves down the fallopian tube and into the uterus.It is also called uterine tubes or oviducts, these tube-like structures that open into either side of the females’ uterus are powerful because they transport the ova from the ovary to the uterus each month.
Salpingectomy is preferred over salpingostomy (also called neosalpingostomy or the process of creating an opening into the fallopian tube ) to treat the buildup of fluid (hydrosalpinx) in a fallopian tube.