Types
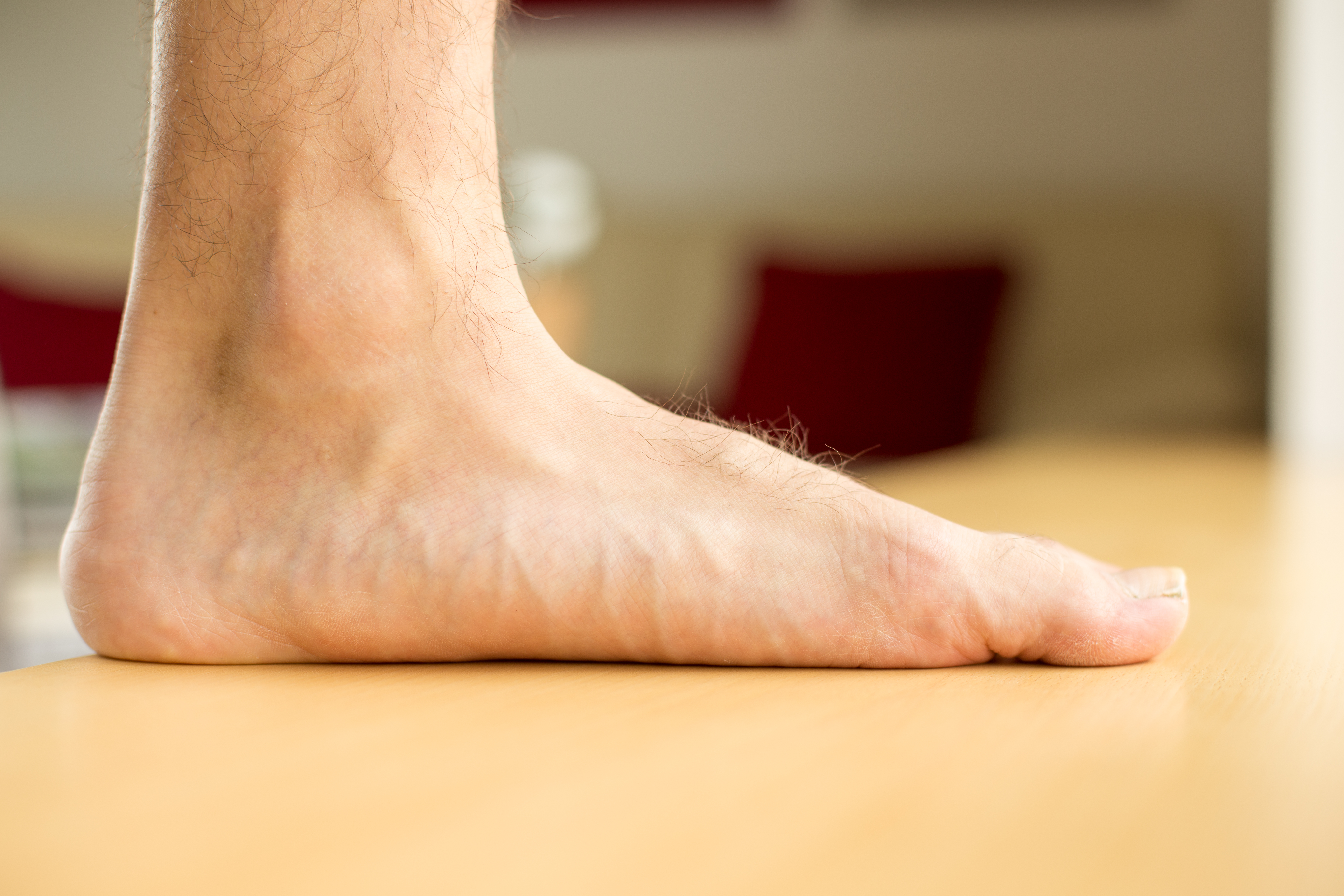
Flexible flatfoot
This is also called “pediatric flatfoot” because it is first obvious during the formative years. Congenital or flatfoot (talipes planovalgus) is common in children. Nearly all babies appear to have flat feet due to the fat pads on the soles of their feet, and that the arch does no longer grow until 5 or 6 years of age.
Flexible flatfoot is typically in both feet and posterior tibial tendon dysfunction or adult-acquired flatfoot can occur in one or both feet.
Rigid flatfoot
This form of flatfoot develops because of the weakening of the tibialis posterior muscle tendon, which helps shape the foot arch. It is a situation that ends in flattening of the arch and rolling in of the ankle. It is a deformity with early symptoms of pain and swelling at the internal arch of the foot that progress to the outside of the foot under the ankle. It also results in arthritis of the foot and ankle joints.
Symptoms
A flat foot can cause no signs. Symptoms of flat foot consist of pain that may be in the internal arch, heel, or ankle and at the outer part of foot below the ankle. Flattening of the arch can lead to rolling in of the foot and ankle and tilting outward of the heel. Flatfoot can also cause shin pain (shin splints), and pain of the knee, hip, and/or lower back.