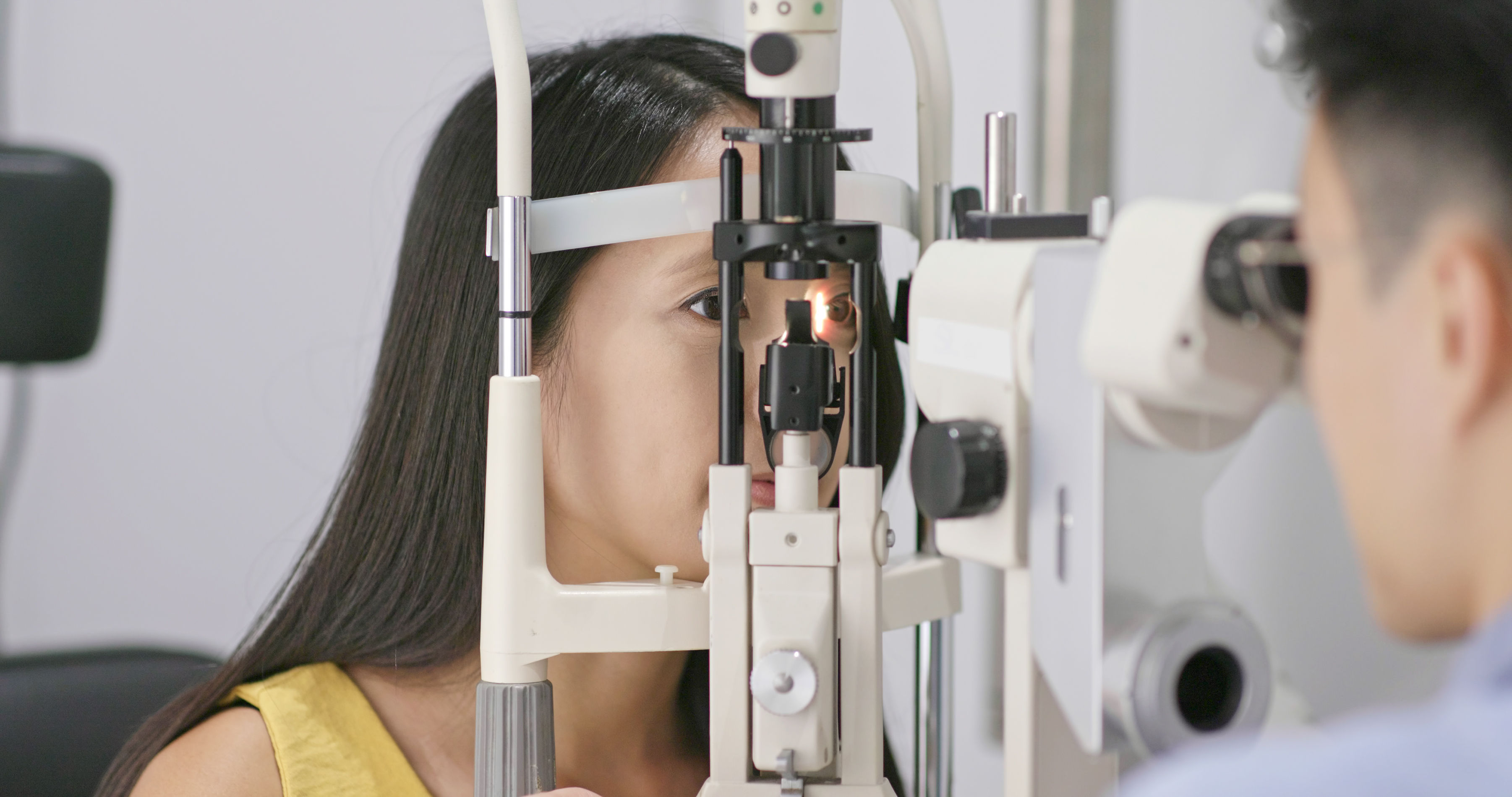
Tonic pupil syndrome is a rare neurological disorder that affects the pupil of a patient’s eye. In most patients, the pupil is dilated and sluggish to respond to light in proximity. In other patients, the pupil might be constricted rather than dilated. Inferior or rather absent reflexes are also correlated with this disorder. Tonic pupil syndrome does not progress, nor it is life-threatening, or debilitating.
Tonic pupil syndrome’s clinical presentation typically is characterized by at least one of the following: abnormally dilated pupil which does not constrict in response to light, absence of deep tendon reflexes, abnormalities of sweating, and hyperopia.