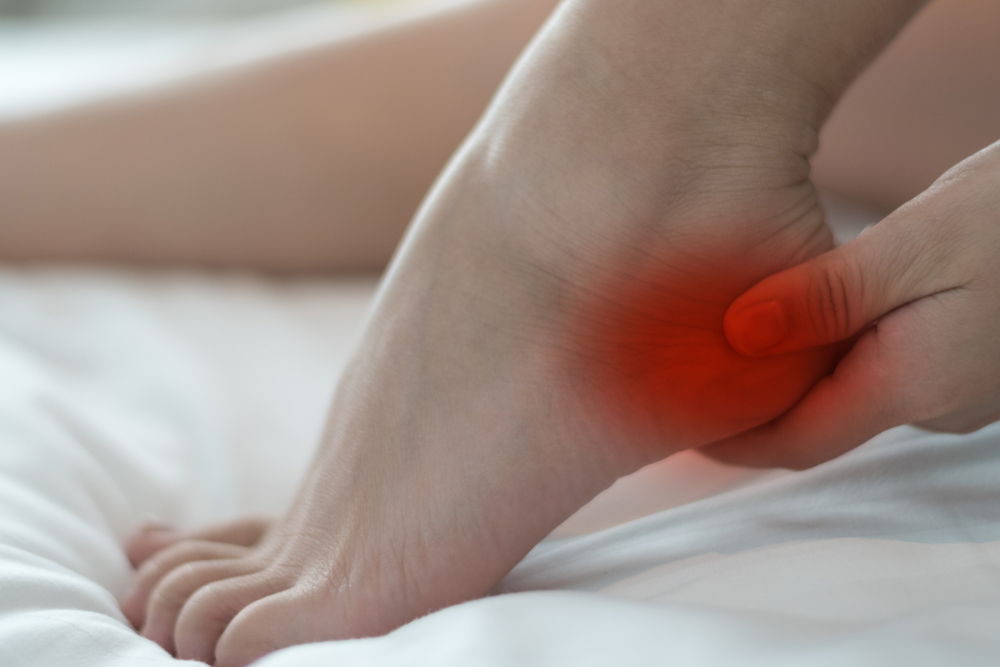
Sever’s condition is an inflammation, irritation, and swelling of the epiphyseal plate in the heel. The epiphyseal plate is a surface of cartilage close to the end of a bone, where the majority of bone development occurs. It is fragile, weak, and more at risk for damage than other bones.
Moreover, Sever’s condition occurs during the rapid growth of puberty. At this time, the muscles, tendons, and bones develop at different rates. The tendons and muscles could become tight, dragging on the epiphyseal plate in the heel.
Furthermore, sports and activities pull on the tight tendons and muscles, harming the epiphyseal plate. This harm leads to the discomfort and pain of the disease.
In some cases, Sever’s disease can occur from standing so long, which creates continuous pressure and force on the heel. However, with good management, this condition will normally go away within a month and not cause severe problems.