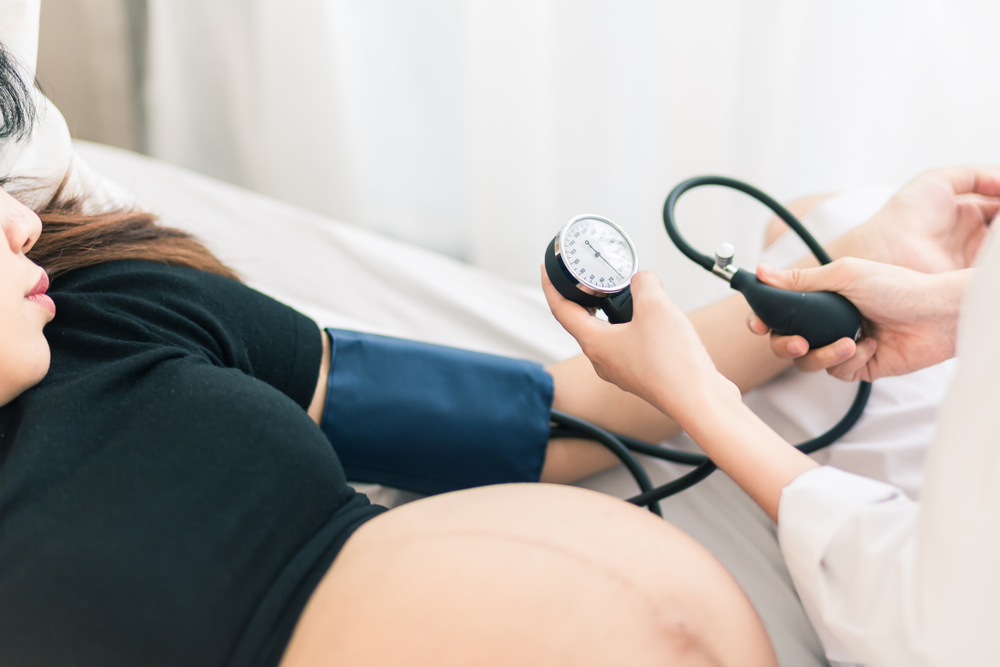
Preeclampsia is a problem that arises during pregnancy that is characterized by hypertension and symptoms of damage to another organ such as the liver and kidneys. Preeclampsia typically starts after 20 weeks of pregnancy in women with previously normal blood pressure.
Left untreated, preeclampsia can prompt serious complications for both you and your baby. If you have preeclampsia, delivery of your baby will stop it. Indeed, even after delivery of the child, it can take a while for you to improve.
If ever you deliver early, you may have complications. Your child needs more opportunity to develop, yet you have to abstain from putting yourself or your infant at risk for complications.
Occasionally, preeclampsia develops after delivery of the child, a condition known as postpartum preeclampsia.