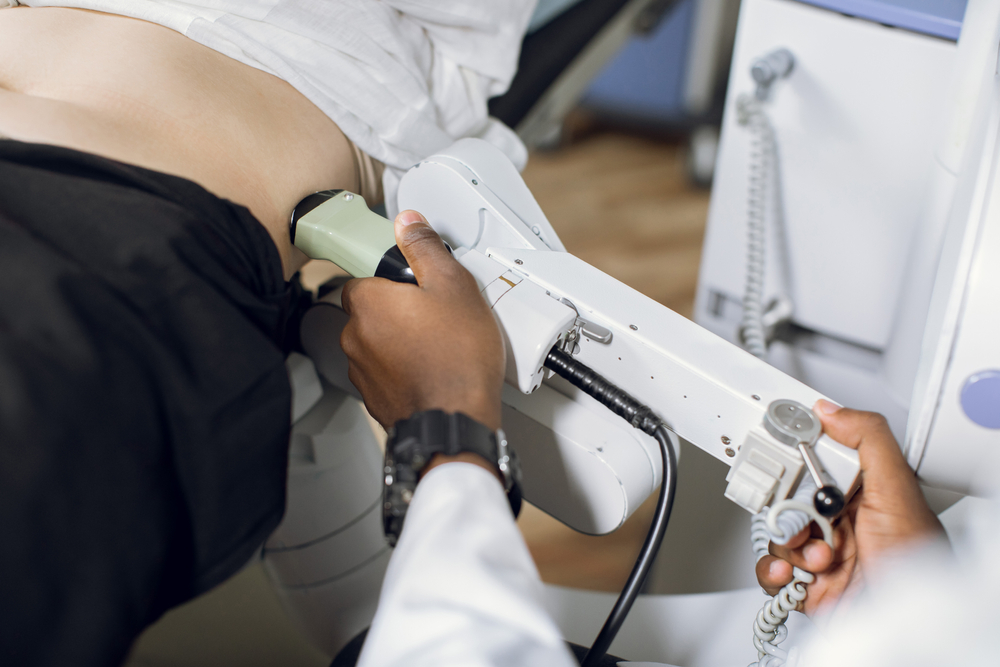
Nephrolithiasis or kidney stones are solid masses of salts and minerals inside the kidneys. It can influence any part of the urinary system— from the kidneys up to the urinary bladder. This is due to diet, obesity, health conditions, and certain medications.
Usually, stones develop when the urine has become concentrated, letting minerals bind together and crystallize. Depending on your condition, you might need only to drink plenty of water to pass the stones and take pain reliever medication. However, for some instances, if kidney stones have been lodged in the urinary system, are connected with a urinary tract infection, or are causing serious problems, surgery may be required.