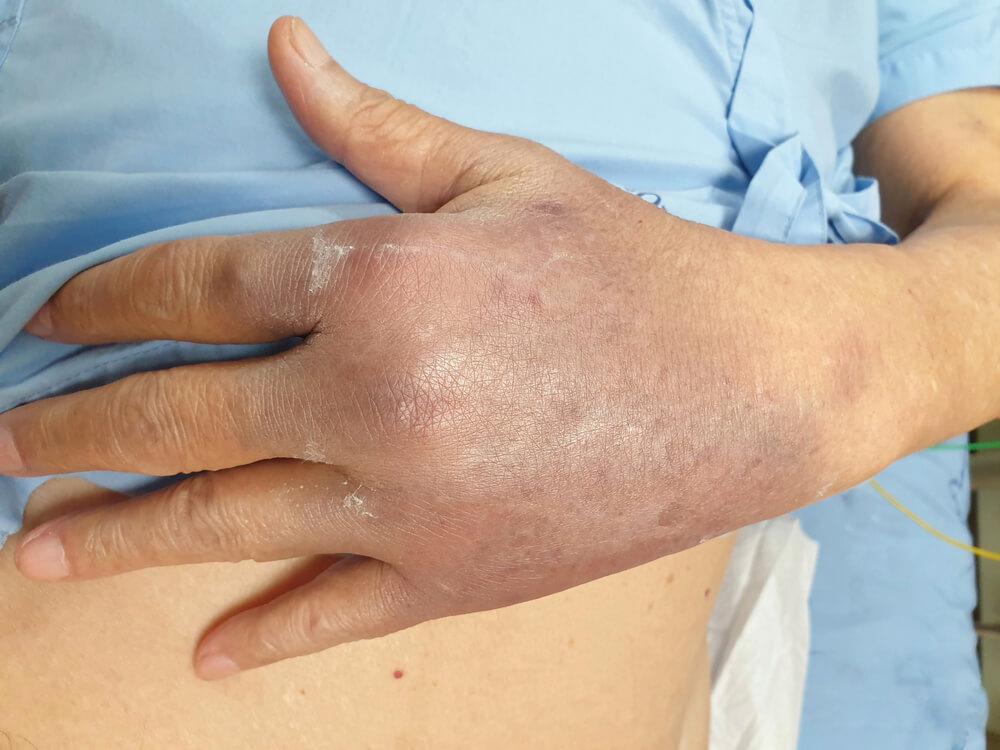
Immune thrombocytopenic purpura or ITP is a condition that can cause immoderate or easy bleeding and contusions. The bleeding results from an uncommonly low range of platelets, which are the cells that help out in forming a blood clot.
Immune thrombocytopenic purpura can make purple contusions, including a small purple-reddish spot that appears as a rash. Children may develop ITP after they experience aggressive infections and commonly recover the entire time without medications. For adults, the disease is frequently prolonged.
If you don’t have any symptoms of low platelets and bleeding, treatment is not necessary. If you have serious symptoms, treatment is necessary to increase your platelet levels or a procedure to remove your spleen may be done.
Immune thrombocytopenia commonly occurs when your immune defense incorrectly strikes and damages platelets, which are cells that aid in blood clot formation.