Hematocrit is the measure of blood that has red blood cells. HCT (hematocrit) uses milliliters as its unit, and it is numerically expressed through a percentage such as if there are 200,000 milliliters of blood and there is a 50% HCT, then there would be 100,000 milliliters.
It can be measured by getting a blood sample that calculates the HCT by the calculation of hemoglobin and the average volume of red blood cells. It doesn’t count everything, but it rather accurately measures it through the blood sample.
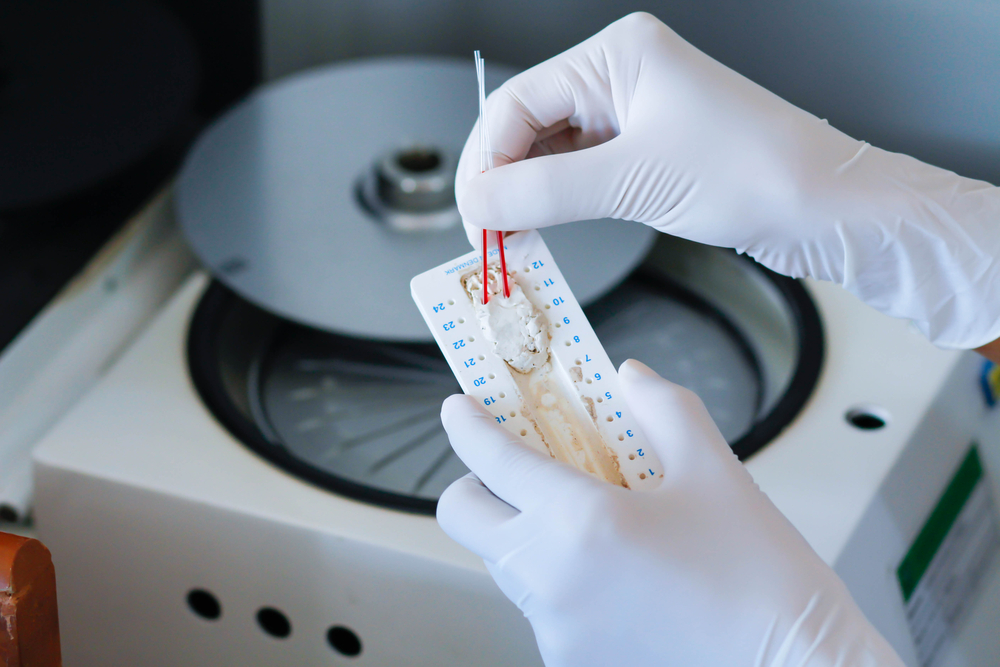
Another way to measure blood is through a centrifuge wherein a tube of blood is centrifuged, and the red blood cells are found in the bottom of the tube. You can see the volume of blood visually after it settles.