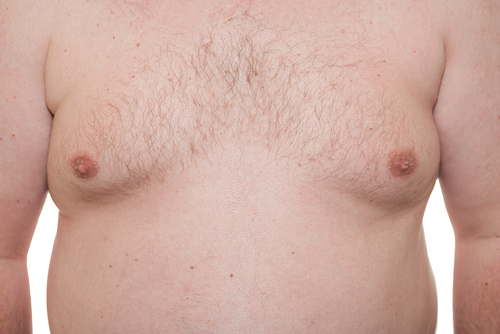
Gynecomastia is swelling of the breast in males. In response to too much estrogen (a female hormone) or too little testosterone (a male hormone), the glandular tissue of the breast swells and forms a breast bud (enlarged breast). Gynecomastia can occur in babies, teen boys, and older men.
Gynecomastia usually starts as a tender lump below the nipple. The development of breast tissue can occur in one or both side, and can grow unevenly.
What causes gynecomastia?
In newborns, gynecomastia is caused by estrogen from the mother. Breast buds are common in baby boys. Breast buds tend to go away gradually by 6 months of age, but they can last longer in some babies.
In preteen boys, gynecomastia can also be caused by an estrogen-producing tumor. Breast buds are common during puberty. The buds may last up to 2 years, but they tend to go away within the first year.
In teen boys, gynecomastia is caused by the hormonal changes of puberty. Gynecomastia occurs in many boys during early puberty to middle puberty. It usually goes away within 6 months to 2 years.
In adult males, gynecomastia is usually caused by another condition, such as liver or lung cancer, cirrhosis of the liver, overactive thyroid, or by hormone problems, such as cancer of the pituitary gland, adrenal glands, or testicles. Alcohol, marijuana, methamphetamine, and heroin use also may cause gynecomastia.
Use of certain medicines may also cause gynecomastia.