DIAGNOSIS
Choledochal cysts are most commonly diagnosed by ultrasound or prenatal ultrasound before birth. Other imaging tests include CT scans, MRCP or ERCP.
Choledochal cysts are typically diagnosed together of several types:
- Type I: Cyst of the bile duct. This is the foremost common sort of choledochal cyst, accounting for about half all choledochal cysts.
- Type II: Pouching or sac on the common bile duct .
- Type III: Cyst inside the wall of the duodenum or pancreas.
- Type IV: A cyst that extends into the liver along the bile ducts.
- Type V: Multiple cysts along the common bile duct inside the liver, also referred to as Caroli’s Disease.
If not given immediate medical care, complications of these diseases includes:
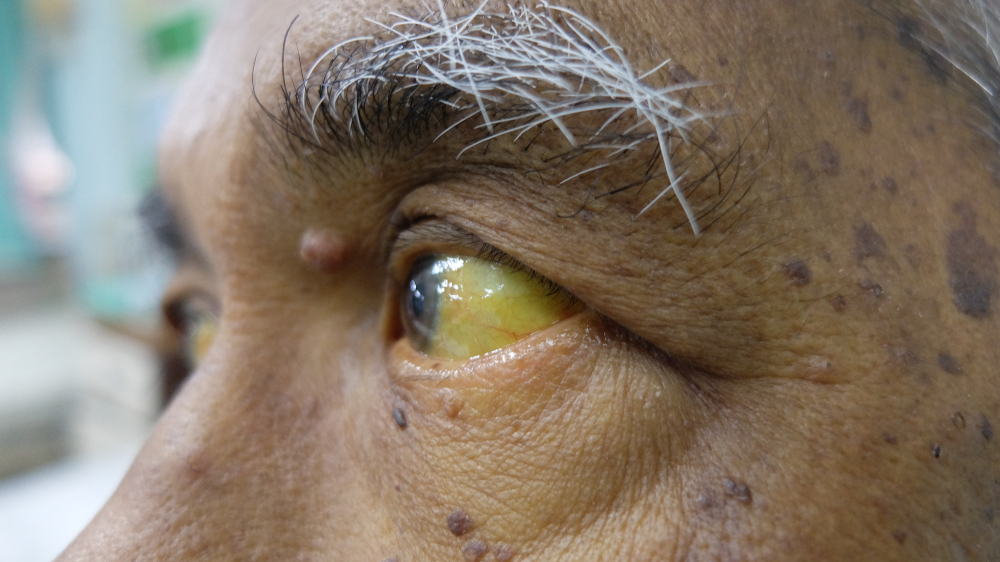
- Infection
- Jaundice
- Pancreatitis
- Gallstones and sludge within the common bile duct and gallbladder
- Gastrointestinal (GI) obstruction
- Cirrhosis of the liver
- Malignancy
TREATMENT
Choledochal cysts are typically treated surgically, either by an open surgery (using one incision) or laparoscopically, where small incisions and a camera are to guide the surgeon. Both procedures are performed in the operating room under general anesthesia. In both sorts of surgery for choledochal cysts, the cyst is removed and sometimes the system of bile ducts are reconstructed or repaired employing a section of intestine. Primary care physicians who encounter a patient with a choledochal cyst should consult a surgeon.