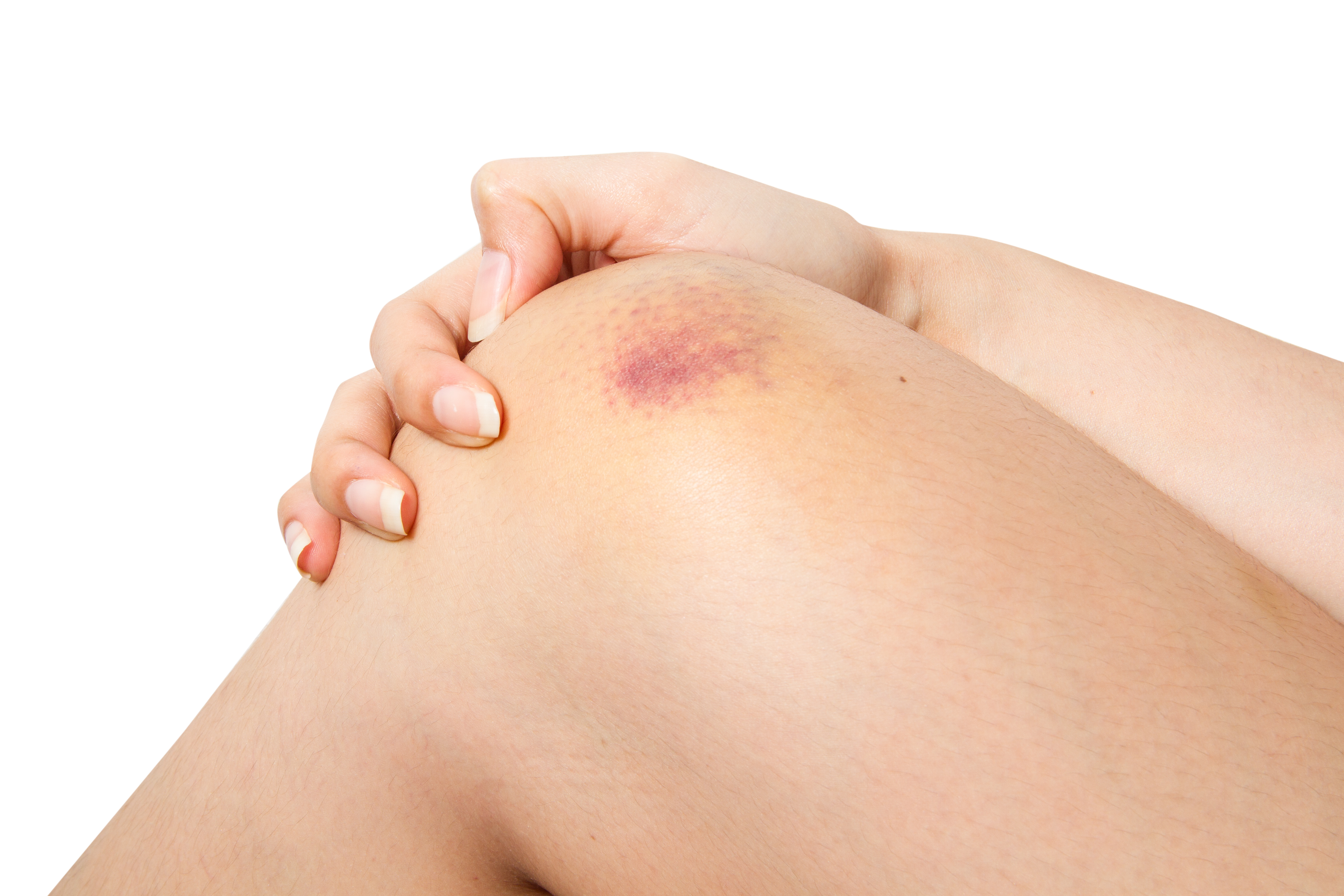
A bruise is a common skin injury that results in a discoloration of the skin. Medically, it is known as a contusion. It occurs when tiny blood vessels are damaged or broken as the result of trauma to the skin. The raised area of a bump or bruise is caused by leaking from these injured blood vessels into the tissues as well the body’s response to the injury.
Causes of a Bruise
People typically get bruises when they bump into something or when something bumps into them.
- Bruises can occur in some people who exercise vigorously, such as athletes and weight lifters. These bruises result from microscopic tears in blood vessels under the skin.
- Unexplained bruises that occur easily or for no apparent reason may indicate a bleeding disorder, especially if the bruising is accompanied by frequent nosebleeds or bleeding gums.
- Often, what are thought to be unexplained bruises on the shin or the thigh, for example, actually result from bumps into a bedpost or other object and failing to recall the injury.
- Bruises in elderly people frequently occur because their skin has become thinner with age. The tissues that support the underlying blood vessels have become more fragile.
- Bruises are also more common in those taking medicine to thin the blood.